Ultimate Credit Card Processing Terminology Glossary
Last Updated on December 13, 2022 by Corepay
Credit card processing terminology can be confusing; however, it is something that all merchants should have a solid understanding of. When applying for a new merchant account, businesses will want to have a payments ally who understands the language they see on their processing statements.
While most statements will contain straight-forward terminology, there are many terms and phrases that merchants likely will not be familiar with.
Have you ever received a statement and find yourself wondering how to read it or are confused by some of the terminology? You’ve come to the right place.
In this article, we will lay out all of the most important credit card processing terminology to understand what you are looking at when you assess a statement.
Here is a quick infographic that sums 30 great credit card processing terminology. If you enjoy the images, feel free to use them, just give credit to Corepay by linking to this article.
Credit Card Processing Terminology All Merchants Should Know
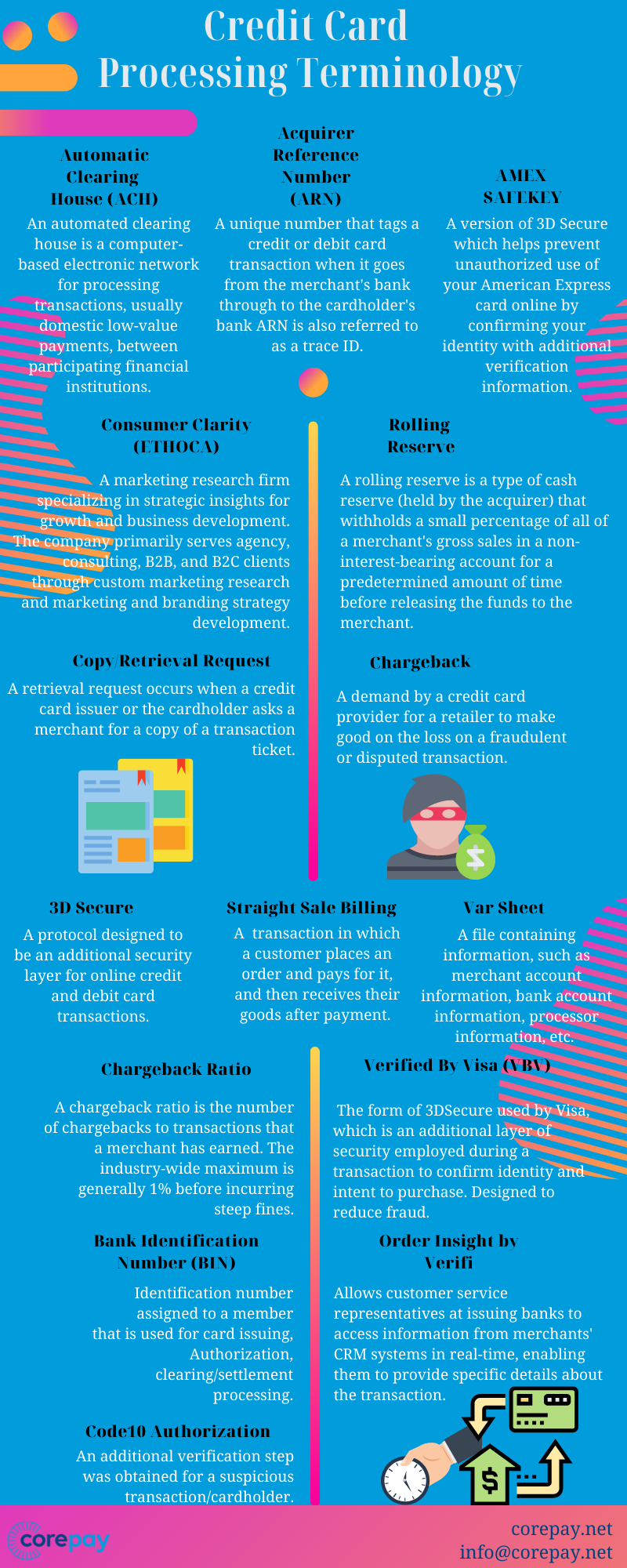
Automatic Clearing House (ACH) – ACH A network used for electronically moving money between bank accounts across the United States. The fund’s transfer system is governed by the rules of the National Automated Clearing House Association.
Approval Codes – Authorization code indicating the transaction is approved and can be processed.
Authorization Code – A code sent by the Issuer in response to the authorization request indicating whether the transaction was approved. These will read: approved, declined/declined pick-up.
Address Verification System (AVS) – A tool that enables merchants to detect suspicious card transactions/prevent credit card fraud. This ensures the address used in the transaction/order matches the address on file with the issuer.
Acquirer Reference Number (ARN) – A unique number that tags a credit or debit card transaction when it goes from the merchant’s bank through to the cardholder’s bank. This number is often used to determine where a transaction’s funds lie at a certain time. ARN is also referred to as a trace ID.
AMEX SAFEKEY – A version of 3D Secure which helps prevent unauthorized use of your American Express card online by confirming your identity with the additional verification information.
Balance – Amount owed by the cardholder to the issuer.
Batch – Accumulated card transactions stored in the terminal or host computer.
Bank Identification Number (BIN) – Identification number assigned to a member that is used for card issuing, Authorization, clearing/settlement processing.
Card Not Present (CNP) A transaction in which the card is not present. (Online purchases, for example).
Card Present Transaction (CPT) A transaction in which the card is physically present. (Eg. Paying for groceries in-person).
Chargeback – A demand by a credit card provider for a retailer to make good on the loss on a fraudulent or disputed transaction.
Chargeback Ratio – A chargeback ratio is the number of chargebacks-to-transactions that a merchant has earned. The industry-wide maximum is generally 1% before incurring steep fines.
Code10 Authorization – An additional verification step obtained for a suspicious transaction/cardholder.
Custom Payment Service – Visa’s regulations for information that must be submitted per transaction.
Card Verification Value 2 (VISA) – Values used as a security feature for verifying credit cards while making CNP transactions (found as a three-digit code on the back of the card).
Card Validation Code 2 (Mastercard) – Values used as a security feature for verifying credit card while making CNP transactions (found as a three digit code on the back of the card).
Card Identification Number (American Express) – Equivalent to VISA/MC as an additional security feature. Found as a four-digit card verification value found on the front of the card.
Copy/Retrieval Request – A retrieval request occurs when a credit card issuer or the cardholder asks a merchant for a copy of a transaction ticket.
Consumer Clarity (ETHOCA) – A marketing research firm specializing in strategic insights for growth and business development. The company primarily serves agency, consulting, B2B, and B2C clients through custom marketing research and marketing and branding strategy development.
Doing Business As (DBA) – The trade name (and often descriptor) of a Merchant that may appear on business signs, customer literature, or other documents.
Decline Code – An Authorization Code indicating that the transaction is declined, along with any details available as to why the transaction was not allowed to proceed.
Decline Pick Up Code – An Authorization Code indicating that the transaction is declined and the card should be retained by the merchant due to confirmed fraud.
Demand Deposit Account – A commercial banking account designated by the merchant through which all transactions, fees, charges, adjustments, and chargebacks can be processed.
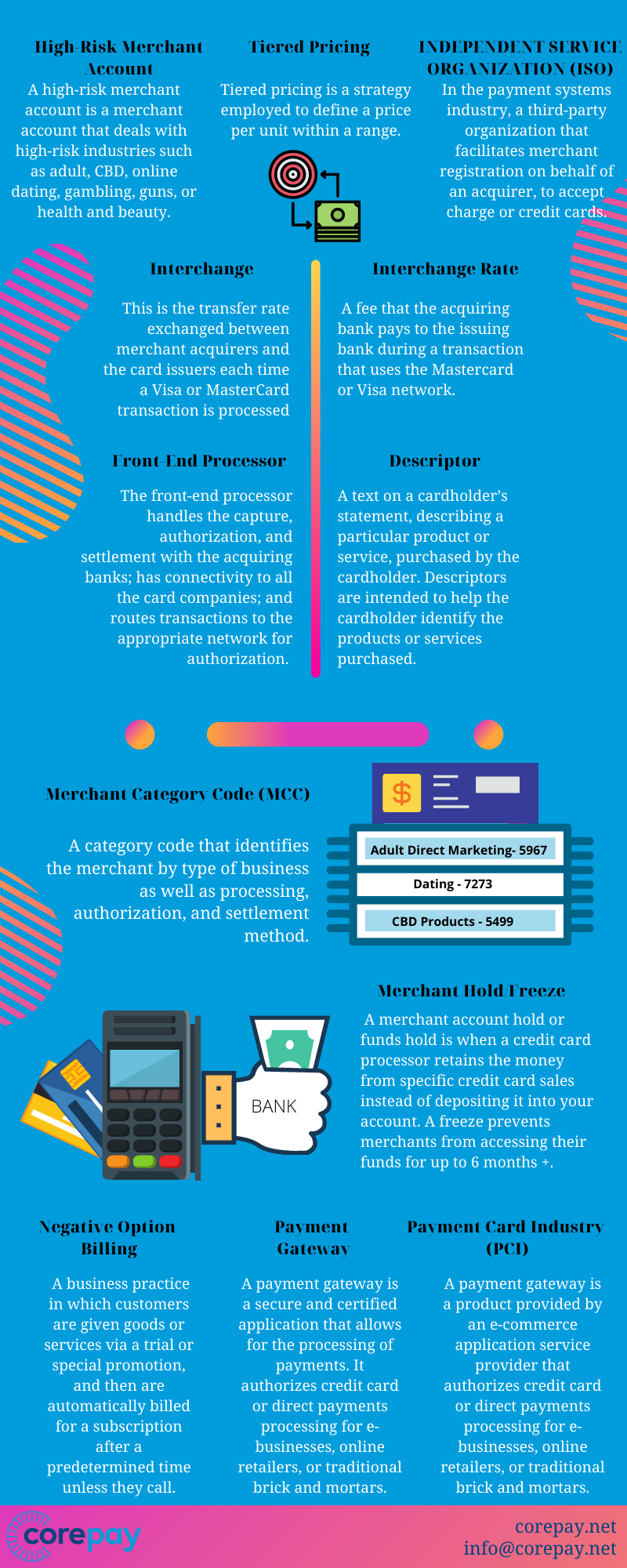
Descriptor – A text on a cardholder’s statement, describing a particular product or service, purchased by the cardholder. Descriptors are intended to help the cardholder identify the products or services purchased.
Discount Rate – A type of fee paid by a merchant to process its card transactions. The fee is calculated by multiplying the Discount Rate by the volume of card transactions.
Electronic Benefit Transfer (EBT) – An electronic system that allows a recipient to authorize a transfer of their government benefits from a federal account to a retailer account to pay for products received.
Embossing – The process of printing data on a card in the form of raised characters to allow the imprinting of transaction receipts.
ELECTRONIC DRAFT CAPTURE (EDC) – An EDC (electronic data capture) works to make use of POS (point of sale) terminals for credit card processing in addition to its submission with the eCommerce providers of merchant accounts or other types of credit card processors.
Encryption – A security or anti-fraud technique that scrambles data automatically in the terminal before any data is transmitted.
EURO MASTERCARD VISA (EMV) – EMV is short for Europay, MasterCard, and Visa, the 1994 founders. It commonly refers to a credit card with a smart chip.
EXTENSIBLE MARKUP LANGUAGE (XML) – A metalanguage (a language to define languages) approved as a World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) recommendation in February 1998.
Factoring – Another term for laundering through someone else’s merchant account, or processing goods/services other than what was approved by the acquiring bank.
FLOOR LIMIT – An amount that Visa and MasterCard have established for single transactions for specific types of Merchants, above which an authorization code is required.
FRAUDULENT TRANSACTION – A transaction unauthorized by the cardholder.
Fraud Ratio – Fraud ratio is a fraud alert-to-sale calculation. Fraud Ratio varies between major credit card brands. For Visa – the fraud alerts amount received in the given calendar month is divided by the amount of sales from the same month. For Mastercard – the fraud alerts amount received on sales in the given calendar month is divided by the amount of sales from the same month.
Front-End Processor – The front-end processor handles the capture, authorization, and settlement with the acquiring banks; has connectivity to all the card companies; and routes transactions to the appropriate network for authorization. In the USA, some examples of front-end processors are TSYS and First Data.
Fulfillment House – A business that provides services of storage, breaking bulk, unpacking, re-packing and making (or arranging) subsequent delivery to its clients’ customers of goods imported from outside the EU, which have been cleared for customs purposes.
Hologram – A three-dimensional image included on a Card to discourage counterfeiting.
Host – Central server used to store information between merchant and the issuer.
High-Risk Merchant Account – A high-risk merchant account is a merchant account that deals with high-risk industries such as adult, CBD, online dating, gambling, guns, or health and beauty.
Imprint – The physical impression made from a Card on the transaction receipt may prove that the card was present when the sale was made.
INDEPENDENT SERVICE ORGANIZATION (ISO) – In the payment systems industry, a third-party organization that facilitates merchant registration on behalf of an acquirer, to accept charge or credit cards.
Interchange Rate – A fee that the acquiring bank pays to the issuing bank during a transaction that uses the Mastercard or Visa network.
Interchange – This is the transfer rate exchanged between merchant acquirers and the card issuers each time a Visa or MasterCard transaction is processed – see interchange fees
Independent Sales Organization (ISO) – An ISO refers to an independent sales organization that has an agreement to sell the services of a bank and is allowed to mark up the fees and recruit merchants.
Interchange Pass-Through – A merchant account that uses an Interchange Pass Through pricing method applies processing fees by adding a small percentage to the actual interchange
Issuing Bank – The bank or financial institution that extends credit to a cardholder through the issuance of a branded payment card for use in the payment of goods and services.
JCB – Formerly Japanese Credit Bureau, is a credit card company based in Japan.
Magnetic Stripe Reader – A device that reads the encoded magnetic stripe information from the bank card when swiped through the unit.
MASTERCARD CHARGEBACK MONITORING PROGRAM – MasterCard reviews merchant chargeback activity with its Excessive Chargeback Program. Mastercard expects merchants to engage in all best practices to minimize disputes and reduce chargebacks.
MASTERCARD SECURE CODE – a secure online payment service available only for MasterCard credit cards. It uses the 3D Secure (3DS) payment system to verify your identity as the owner of your card.
Merchant Category Code (MCC) – A category code that identifies the merchant by type of business as well as processing, authorization, and settlement method.
Merchant – A company that has been approved by an acquirer to accept credit card transactions.
Merchant Account – An account opened by a business that wishes to accept credit card payments. It is opened through a bank/credit processing company.
Merchant Hold/Freeze – A merchant account hold or funds hold is when a credit card processor retains the money from specific credit card sales instead of depositing it into your account. A freeze prevents merchants from accessing their funds for up to 180 days.
Merchant Identification Number (MID) – A unique number generated by a processor or acquirer for each merchant location.
Merchant Processing Agreement (MPA) – The written agreement between merchant and acquirer that details their rates, rights, and regulations in the contract.
Monthly Minimum Fee – A minimum amount in fees that your member service provider may require you to generate each month.
MOTO – Refers to mail order/telephone order, which are credit card transactions that take place via e-mail, fax, mail, or telephone.
Multi-Currency Processing – Multi-currency payment processing occurs when your business can accept credit cards from customers in foreign currencies.
Non-Qualified Rate – highest percentage rate a merchant will be charged whenever they accept a credit card in a tiered pricing structure
Negative Option Billing – Negative Option Billing – A business practice in which customers are given goods or services via a trial or special promotion, and then are automatically billed for a subscription after a predetermined time unless they call.
Offline Sale – Credit card machine has no communication method to process an online transaction. Transaction date is stored and then transmitted once the connection is reestablished
Original Draft – The actual merchant copy of the receipt used in the transaction. This can be requested when dealing with a chargeback dispute.
Order Insight (a Verifi solution)- allows customer service representatives at issuing banks to access information from merchants’ CRM systems in real-time, enabling them to provide specific details about the transaction.
Payment Gateway – A payment gateway is a secure and certified application that allows for the processing of payments. It authorizes credit card or direct payments processing for e-businesses, online retailers, or traditional brick and mortars.
Payment Card Industry (PCI) – Strict requirements set forth by the PCI council which details measures that payment processors must take to help prevent fraud in credit card processing.
Point Of Sale (POS) – The physical device in a store or retailer which allows the acceptance of credit/debit cards.
Payment Processor – A payment processor is a company (often a third party) that acts as an intermediary between the authorization request from a point-of-sale device and the card payment brands.
Per Transfer Fees – Also known as authorization fees. transaction fees paid by the merchant to the merchant bank or other contracted party on a per-transaction basis.
Qualified Rate – Part of a tiered billing structure. This rate is often the rate that is advertised as it is the lowest merchants can pay in fees per transaction.
Quasi Cash – Transactions representing a merchant’s sale of items that are directly convertible to cash.
Quick Payment Service – Interchange program developed for convenience-oriented business such as fast-food restaurants and movie theaters.
Referral Code – An Authorization Code indicating that the issuer is requesting the merchant to call the Voice Authorization Center – additional information will be requested.
Retail Merchant – A merchant that provides goods/services in a retail setting.
Real-Time Processing – The process where a customer’s credit card is authorized and charged at the time of purchase.
Rolling Reserve – A rolling reserve is a type of cash reserve (held by the acquirer) that withholds a small percentage of all of a merchant’s gross sales in a non-interest-bearing account for a predetermined amount of time before releasing the funds to the merchant.
Retrieval Request – When a customer requests additional information on a transaction after viewing credit card statement.
Reversal – An online financial transaction used to negate or cancel a transaction that has been sent through interchange in error.
Recurring Billing – Recurring billing happens when a merchant automatically charges a customer for goods or services on a prearranged schedule. Recurring billing requires the merchant to get the customer’s information and permission. An example of this would be any subscription box service.
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) – a cryptographic protocol that provides secure communications on the internet for such things as web browsing, e-mail, and eCommerce transactions.
SE Number – Service Establishment number unique to a merchant provided by American Express.
Service Provider – The company that processes transactions for the merchant.
Settlement – Also known as batch settlement. The process in which incoming transaction totals are verified and collected.
Straight Sale Billing – a transaction in which a customer places an order and pays for it, and then receives their goods after payment.
T&E Merchant – Travel and entertainment merchant (airlines, car rental company/hotels).
Terminal – A device used by the merchant to electronically process transactions.
Tiered Pricing – Tiered pricing is a strategy employed to define a price per unit within a range.
Terminal Identification Number – The Terminal Identification Number (TID) is a POS device’s unique identification number assigned by a merchant’s processor.
Validation Code – A 4 digit unique code that Visa provides.
Value Added Reseller – A third-party vendor that enhances or modifies existing hardware or software, adding value to the services provided by the processor or acquirer.
Var Sheet – A file containing information, such as merchant account information, bank account information, processor information, etc. This file is typically given to a payment gateway, allowing for communication between the gateway and the merchant account provider.
Verified By Visa (VBV) – The form of 3DSecure used by Visa, which is an additional layer of security employed during a transaction to confirm identity and intent to purchase. Designed to reduce fraud.
Virtual Terminal – This is an application that allows merchants to manually key in customers’ credit card information. All of this information is then transmitted and authorized by a payment gateway.
Visa Dispute Monitoring Program – The Visa Dispute Monitoring Program, or VDMP, gives Visa a way to monitor chargeback activity at the merchant level. VDMP is forced on merchants who are deemed as having an unacceptably high chargeback to sales ratio and is something merchants should proactively attempt to avoid participating in.
3D Secure – A protocol designed to be an additional security layer for online credit and debit card transactions. The name refers to the “three domains” which interact using the protocol: the merchant/acquirer domain, the issuer domain, and the interoperability domain.
We hope you enjoyed this list of credit card processing terminology.
We appreciate you following Corepay’s blog. Let’s collaborate, send us your article suggestions, questions, and/or feedback to: [email protected].
