Payment Processor VS Payment Gateways – Which To Pick
Last Updated on January 14, 2022 by Corepay
If you are in eCommerce, you have likely heard about payment gateways and payment processors. With this being said, payment processors and payment gateways are not the same things yet are both needed during an online transaction.
Should you have landed on this page looking for answers regarding payment gateways/processors and you’re confused about the difference and what you need for your business, you’ve come to the right place.
This article will break down everything you need to know about payment processors vs. payment gateways so that you will have an understanding of what your business needs to succeed online.
NOTE: IF YOUR BUSINESS DEALS WITH E-COMMERCE OR PHONE SALES, YOU NEED A RELIABLE PAYMENT GATEWAY AND PAYMENT PROCESSOR
Should you be operating an eCommerce store, we highly recommend checking out our eCommerce merchant account solutions.
Payment Processors Vs. Payment Gateways
The easiest way to decipher between a processor and a gateway is that the payment gateway acts as an online point of sales system whereas, the payment processor transmits the data between the customer, the merchant, and the issuing bank.
Who Are The Parties Involved In A Credit/Debit Card Transaction?
To better understand payment processors and payment gateways, let’s look at the parties involved in a standard credit transaction. This will help when we break down the critical difference between gateways and processors later on.
Upon payment from the customer to a merchant, a few different parties will send payment information. We also strongly recommend checking out our complete credit card processing terminology article.
- Issuing bank: An issuing bank is a bank that issued the customer’s credit card. When the customer uses the credit card, the issuer deducts the amount of the transaction from the customer’s account and pays the funds to the acquiring bank.
- Card Networks: The card network is simply the credit card brands such as American Express, Mastercard, or Visa. Each card network sets its own interchange rates, which is the percentage of each transaction you pay for the ability to accept credit/debit cards.
- Payment Processor: The payment processor is the company responsible for transmitting the merchant’s purchase amount and merchant information to the issuing bank, enabling it to pay the acquiring bank.
- Payment Gateway: The payment gateway is a virtual point of sales system that encrypts credit card information and sends it to the credit card processor.
- Acquiring Bank: An acquiring bank contracts with the merchant to accept funds processed by credit/debit cards. Funds are stored in a merchant account and settled to the merchant’s bank account.
What Is A Payment Processor
Your payment processor is perhaps your most important relationship when it comes to operating an online business. The payment processor you choose is responsible for the payment data amongst the following four parties:
- customer
- customer’s bank
- merchant
- merchant’s bank
Payment processors are also usually responsible for any payment processing equipment used to accept credit card transactions.
Payment processors are also typically the supplier of the merchant account for merchants.
All businesses looking to accept payment via online, over the phone, or from a retail store will need to partner with a payment processor.
Your payment processor will handle the credit/debit card transactions for your entire business. Payment processors move funds from one account to another.
Generally, payment processing fees will vary from provider to provider. Certain processors will charge different rates based on the volume of transactions and the level of risk your business operates within.
What Is A Payment Gateway?
Payment gateways facilitate card, not present/online transactions. They are the technology that creates a secure connection between a merchant’s website and a credit card processing company.
A payment gateway processes credit cards online through websites by securely validating the customers’ credit card details and enabling merchants to get paid.
Most payment gateways will have an interface where you can manually enter credit card information for phone sales, also known as a virtual terminal.
So, How Do Payment Gateways Work?
- Consumer purchases with a credit/debit card and enters credit card info
- Merchant’s site sends payment info through their webserver/payment gateway encrypts data
- Payment gateway sends the request to issuing bank
- Bank verifies funds and authorizes payment to go through
- Payment gateway sends funds to the merchant
Typically, payment gateways can be set up through a merchant’s chosen credit card processing company. If you go the all-in-one route, you can avoid compatibility issues where your payment gateway provider and payment processor aren’t compatible.
At Corepay, we have our payment gateway, Solidgate, explicitly built for high-volume eCommerce. We are also partnered with some of the largest payment gateways available to ensure our clients can offer the lowest prices with the best service.
Do I Need A Payment Gateway And A Payment Proccessor?
If your business is entirely online, the answer is yes. Should you be accepting credit cards at the point of sale, such as a retail store, you can typically skip a payment gateway .
Do All Online Stores Require The Same Services?
Not every online business is created equal. The type of payment processor you choose depends on a few different factors including, fees, risk, and specific services you require.
For example, you will need to find a payment processor specializing in high-risk, preferably with experience in your specific niche if you are deemed high-risk.
When online stores face a high number of chargebacks, they typically will pay more in fees and will also have to explain why their chargebacks are high and a plan to improve them.
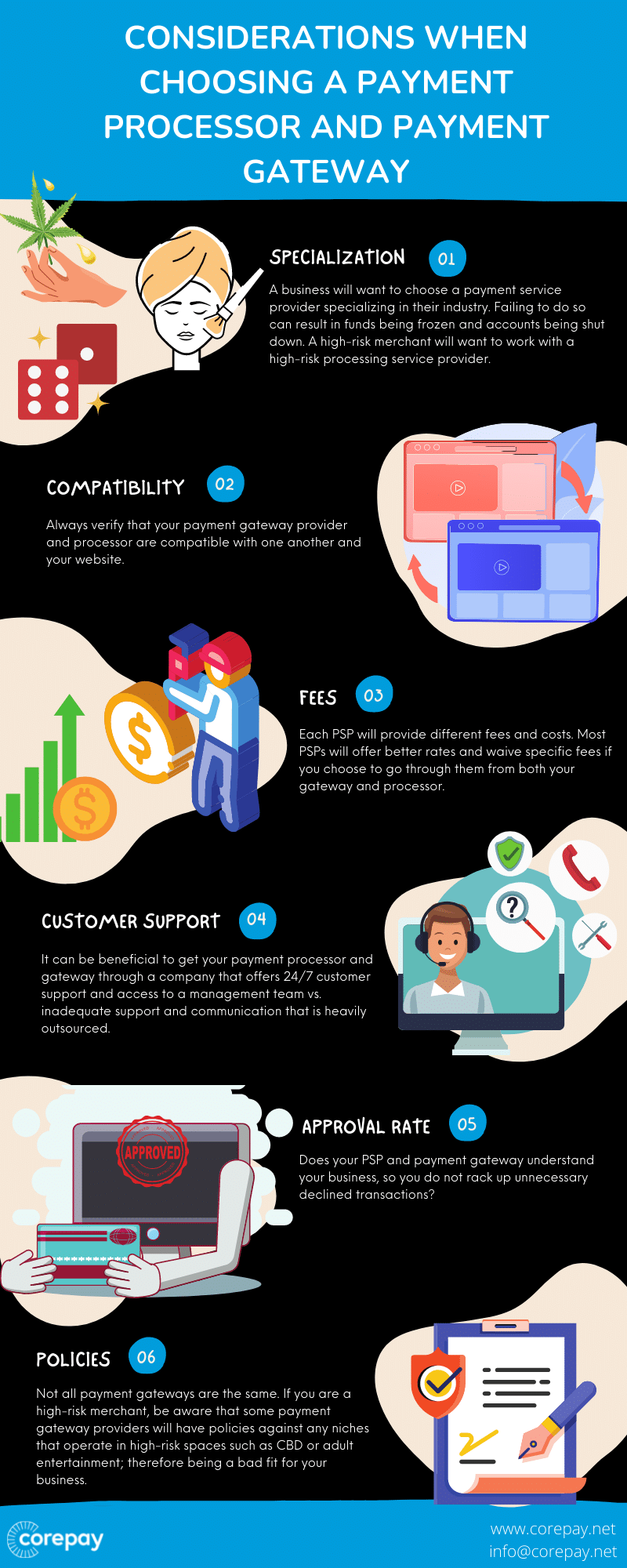
Choosing A Payment Processor And Payment Gateway
Choosing the correct payment processor and configuring a payment gateway is exciting; however, it is often confusing and complicated at first. In addition, fees can vary heavily from processor to processor and pricing models, features, and services offered.
When choosing your payment services provider, make sure they specialize in the industry you operate in. Also, be aware that some PSPs can provide you with payment processing and a payment gateway either through their service or third-party when others cannot.
Always verify that your payment gateway provider and processor are compatible with one another and your website.
The following are key points to consider when choosing a PSP:
- Fees: Compare costs and fees from one provider to the next
- Services provided: What does your PSP provide to your business?
- Forms Of Payment/Currencies: Can your business accept as many forms of currency as possible?
- Security: Is your payment structure secure?
- Approval Rate: How fast are you able to get approved and begin processing transactions?
- Customer Support: 24/7 customer support is important when it comes to finding the right PSP.
Is Paypal A Payment Gateway?
Paypal is known as a payment aggregator. A payment aggregator is a payment service provider that allows merchants to accept debit or credit card e-commerce payments without going through a bank.
Paypal is one of the most popular payment gateways on the internet, and it is technically a merchant account. With this being said, Paypal has strict policies and is against any niches that operate in high-risk spaces such as CBD or adult entertainment.
Should you choose Paypal for your payment processing needs, be sure that you are not deemed high-risk and do not violate their terms of service.
Should you do so, your account will be frozen or terminated, with funds being held for up to 180 days. Should your account currently be frozen with Paypal, it is best to quickly find another payment processor who specializes in your niche while Paypal finishes its audit of your account.
Unlike payment processors, aggregators generally offer fixed rates, so even as your transaction volume increases, the price you pay does not increase. On the other hand, payment processors typically offer more favorable rates to businesses with high transaction volumes or high-value transactions.
Keep Your Chargebacks At A Minimum To Avoid Higher Fees
Regardless of the route you choose, make sure you do your part to keep chargebacks at a minimum. This includes studying customer purchasing habits, clearly stating return policies, and implementing chargeback tools.
Wrapping Up
Finding a suitable PSP is vital for online businesses now more than ever before. Having the right credit card processing partner truly makes a significant difference in your overall customer experience.
Now that you understand what payment gateways and payment processors are, you should be able to compare different PSPs and choose the best option that fits your business.
We highly recommend filling out the application below to determine how Corepay can best suit your payment processing needs.
We appreciate you following Corepay’s blog. Let’s collaborate, send us your article suggestions, questions, and/or feedback to: [email protected].